Credit Card Fraud Detection

There are several disadvantages of doing business online, such as frequent fraudulent activities that result in loss of revenue for businesses. Cardholders have securities set in place to protect them from fraud, shifting the liability to the merchants whom the fraudsters purchased from. To protect themselves and the revenue they lose to criminal fraud, merchants must employ effective techniques to detect fraud before they occur. These techniques are often a combination of varying tools, from simple verification checks to advanced tools that use advanced machine learning models to detect the potential of fraud.
Using machine learning, algorithms and models can analyze, read, and understand the trends and history. By doing this, you can be more certain and avoid mistakes in detecting credit card fraud. Machine learning tools require data such as behavioral patterns, product catalogs, user location, and more. Using this information, these tools can tackle issues through pattern recognition and tools for fraud detection and monitoring to determine the legitimacy of these transactions.
Table of Contents
What Is Credit Card Fraud Detection?
Credit card fraud uses stolen card details to complete unauthorized online transactions. It is a form of identity theft wherein fraudsters use stolen information to make purchases. Credit card fraud detection identifies fraudulent attempts at making online purchases and denies the user access to complete the transaction. This means of protection is necessary because the ease of completing an online transaction using credit cards translates to easy theft of credit card information.
Merchants must combine various tools to generate data like geolocation, device identification, IP address, billing address, and transaction history and use them to fight theft. The problem with implementing automated security measures is that they can flag down several legitimate transactions, and customers do not like false positives. Stay on top of this by using manual verification where possible.
Difference Between Credit Card Fraud and Identity Theft?
Credit card fraud is the illegal use of a card by a person not authorized to transact with the card. This transaction occurs without the consent of the actual cardholder. It can be initiated by anyone who has the details of a card, and these details can be acquired through physical petty theft or online means.
On the other hand, identity theft refers to illegal access to an individual’s personal effects like a bank account using their personal information. The thief could decide to request new cards for online transactions without the individual’s knowledge.
Must-Have Tools for Credit Card Fraud Detection in Ecommerce
The security of your website and payment platform is crucial for detecting and preventing fraud. Data security begins with the firewalls added to your website and the SSL encryption. Machine learning is also becoming an essential part of fraud security systems because it offers faster verification and automatic credit card fraud detection using analysis from transaction histories.
Merchants should use tools like the standard verification tools provided by the payment processor, tools from third-party fraud prevention providers, and in-house manual techniques. This system would help prevent consequences like:
- Loss of resources and revenue. In cases of fraudulent purchases, merchants must bear the losses of the transaction (purchased product and shipping fees). To prevent these fees, you must implement the necessary tools to avoid this.
- Chargeback fees. Whether a dispute is resolved or it extends to charge banks, merchants must keep up with these fees through chargeback accounting techniques.
- Increased processing fees. An increase in the number of chargebacks a merchant receives would also affect their chargeback rates. When the rate exceeds 2%, the merchant would be flagged. The higher they go, the higher the processing charge for each online transaction.
- Payment processing account termination. Credit card companies flag your account and deem it “high risk.” It occurs when the merchant’s rates exceed the stipulated charge, and accounts may be terminated.
To prevent these issues from causing issues, merchants should use verification tools and techniques. Some of these tools include:
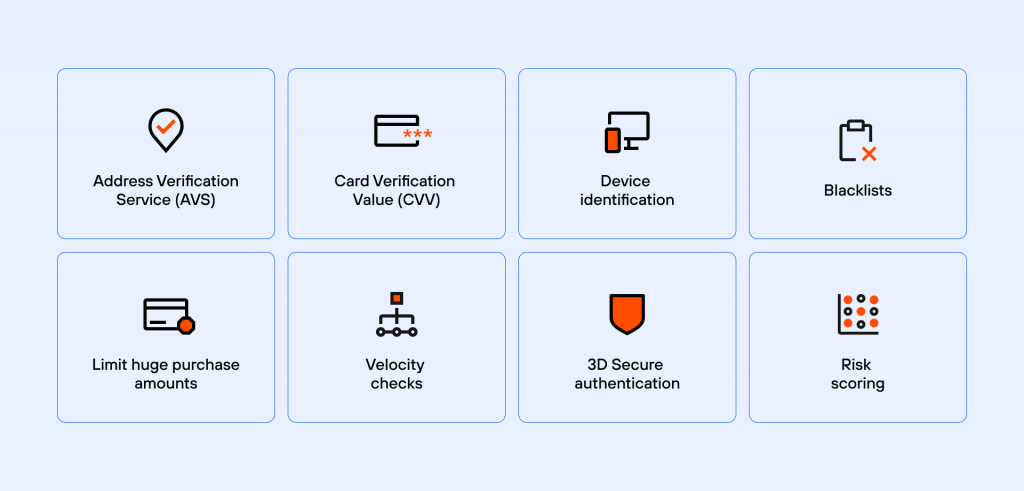
Address Verification Service (AVS)
AVS is a filter that helps in credit card fraud detection by verifying the shipping address and zip code from the transaction by comparing it against the information from the issuing bank. The filter would inform you whether the address and the zip code match. In cases of a partial match (only one information match), you can further investigate using CVV and other tools or decline the transaction.
Capture Card Verification Value Codes (CVV)
CVV is a 3-digit code that is imprinted on the back of all credit cards. Although merchants are not permitted to store this information, it must be provided before the transaction can be processed.
Device Identification
This works by analyzing the device that is used to complete the transaction. It flags devices with a history of fraudulent activities and those that have not been used with the account before. It checks important details and profiles them; these essential details include the system’s operating system and other information that can help in fraud prevention. Every device has a unique fingerprint that can be used to track it online and generate patterns for risk assessment.
Blacklists
After collecting information on fraudulent activities, you can create a blacklist to block transactions with similar details. You can add details like a credit card, email addresses, billing addresses, and high-risk regions, then verify the client’s identity before processing the transaction. This is not a very accurate tool, and merchants need to be wary of using it as it can lead to blocking legitimate transactions.
Limit Huge Purchase Amounts
Stolen credit cards can be noticed and blocked quickly. To take advantage before this occurs, fraudsters try to make big transactions, especially on items with good resale value. You can set limitations using the maximum amount of a transaction, the maximum amount of items that can be purchased at a time, and the maximum number of failed transactions.
Velocity Checks
Fraudsters are innovative, and sometimes, they generate lots of credit card numbers using software and run these numbers for payment until they find the correct one. Velocity checks monitor the number of attempts an account makes and flags it once it exceeds the set number of attempts.
3D Secure Authentication
This is a measure put in place by service providers to add extra security to online card transactions. It can help in verifying a user’s identity, thereby preventing fraud. It is a form of two-factor authentication that requires cardholders to create a secure transaction pin that must be entered before processing a transaction. Incorrect pins would automatically block the transaction, leading to lower chargeback requests.
Risk Scoring
This feature uses data analysis and machine learning to score transactions based on the possibility of fraud. Key points like billing address, IP address, product, amount, and results of verification filters are used to determine the score. You would receive a score and details of the results for each tested component. The higher the score, the higher the probability of fraud. Tools with predictive machine learning models would learn from this analysis and help provide more accurate results in the future.
All these tools are useful for avoiding chargebacks and associated fees. When you pick an automatic credit card fraud detection method, you can reduce the possibilities of credit card fraud, which always leads to an indisputable position.
The Credit Card Fraud Methods
Credit fraud has become a pervasive concern in today’s digital age, costing the US alone $5 billion + per year and fraudsters are constantly evolving their methods to exploit vulnerabilities and deceive unsuspecting businesses. Understanding the various techniques employed by fraudsters is crucial for identifying and preventing credit fraud. See below an overview of some common credit fraud methods, including cards-not-present schemes, new account fraud, credit card skimming, and the takeover of an account.
Cards-Not-Present Schemes
Cards-not-present (CNP) schemes refer to credit card fraud that occurs in transactions where the physical card is not present such as online or over the phone.
Fraudsters obtain credit card information, including the card number, expiration date, and security code, through various means, such as data breaches, phishing, or skimming devices. Then use the stolen card details to make unauthorized online purchases from e-commerce websites or other online platforms. They may create fake accounts or use compromised accounts to conduct these transactions.
Fraudsters may use automated scripts or software to systematically test stolen card information on various websites, looking for vulnerable payment systems where the stolen cards can be used successfully. Then they perform small transactions with stolen card details to check their validity before making larger purchases. These test transactions often go unnoticed by cardholders and are used to verify that the stolen card information is active and valid.
Fraudsters often request that goods or services be delivered to a different address than the billing address associated with the stolen card. This allows them to receive the purchased items without arousing suspicion.
New Account Fraud
New account credit card fraud refers to the creation of fraudulent credit card accounts using stolen or fabricated identities. Here’s an explanation of how it works and some common tricks employed by fraudsters:
- Identity theft: Fraudsters obtain personal information, such as social security numbers, names, addresses, and dates of birth, either through data breaches or phishing schemes. They use this stolen information to create new credit card accounts in the victim’s name.
- Fake documentation: Fraudsters may forge or manipulate documents, such as utility bills or driver’s licenses, to support the creation of a new credit card account. These documents are used to verify the identity of the fraudulent account holder during the application process.
- Synthetic identities: Another tactic is to create synthetic identities by combining real and fake information. Fraudsters may use a legitimate social security number with a different name and address, making it challenging for detection systems to identify the fraudulent activity.
- Credit building: To establish credibility, fraudsters may initially make small purchases and pay off the balance promptly. This helps them build a positive credit history, making it easier to conduct larger fraudulent transactions in the future.
- Rapid spending: Fraudsters often maximize their fraudulent activities within a short period, aiming to exploit the credit line before the suspicious activity is detected. They may make multiple purchases or cash advances in different locations or online stores.
- Changing contact information: To avoid detection, fraudsters may attempt to change the account’s contact information, such as the billing address or phone number, so that any notifications or inquiries regarding the account are redirected to them.
Credit Card Skimming
Credit card skimming is a method used by fraudsters to steal credit card information by illicitly capturing the data from the magnetic strip on the back of a credit card. Skimmers are small devices that can be installed on legitimate card readers, such as ATMs, gas pumps, or point-of-sale terminals, to collect card details without the knowledge of the cardholder. These devices are designed to blend seamlessly with the legitimate card reader, making them difficult to detect.
When a card is swiped or inserted into a compromised skimmer, it captures the cardholder’s data, including the card number, name, and expiration date. In some cases, criminals also use hidden cameras or keypad overlays to capture PIN numbers, enabling them to create cloned cards or conduct fraudulent transactions.
Takeover Of An Account
Account takeover is a credit card fraud method where fraudsters gain unauthorized access to someone’s existing account, typically an online account associated with a credit card or payment service. Once they gain control, they can exploit the account for fraudulent activities, including unauthorized transactions, purchases, or fund transfers.
The process of account takeover often involves various tactics, such as phishing, social engineering, or exploiting weak passwords. Here’s a general overview of how account takeover occurs:
- Phishing: Fraudsters may send deceptive emails, text messages, or make phone calls pretending to be a legitimate institution, such as a bank or e-commerce platform. They trick individuals into providing their account credentials, credit card information, or other sensitive data. Once obtained, the fraudsters use these details to gain unauthorized access to the account.
- Social Engineering: In some cases, fraudsters manipulate individuals into revealing their account details through psychological tactics. They may impersonate customer service representatives, tech support, or even acquaintances to deceive victims into providing sensitive information willingly.
- Weak Passwords: If individuals use weak or easily guessable passwords, fraudsters can exploit this vulnerability by using brute-force attacks or password-cracking techniques to gain access to the account.
How Do Fraud Detection Tools Work?
The previous section discussed various fraud detection tools available to merchants and how they work. Some of these tools use artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect fraud and help you prevent them.
These tools have methods and features that help in user verification and authentication. With access to these kinds of data, you can perform in-depth analysis and create blacklists for locations with a high potential for fraud. You can then manually determine whether you should accept purchases and transactions from these regions.
What Can Merchants Do to Detect Fraud?
There are various steps to take to detect fraud before it occurs. Merchants should employ technological tools for fraud screening and scoring in their fraud management strategies. Analysis and machine learning are also crucial for fraud detection. These features in a tool would automatically analyze data and learn the trends to detect any outliers that may be potential frauds.
Criminal fraud is deemed the merchant’s fault because they are expected to take measures to prevent it from occurring. This type of fraud is costly because a chargeback is inevitable, as the merchant has no means of refuting it. Merchants should use tools, strategies, experience, and professional services.
 PayPal
PayPal Blog
Blog


