How Banks Conduct Transaction Fraud Investigations
Table of Contents
What Are The Different Types Of Banking Fraud?
Bank fraud encompasses a wide range of fraudulent activities targeting financial institutions. Some of the most common types of bank fraud include:
- Account Takeover: Fraudsters gain unauthorized access to a victim’s bank account by stealing credentials or using sophisticated hacking techniques. They then make unauthorized transactions or transfer funds to their own accounts.
- Card Fraud: This involves the fraudulent use of credit or debit card information, such as cloning cards or making unauthorized transactions. It includes activities like skimming, phishing, and card-not-present fraud.
- Identity Theft: Criminals steal personal information to impersonate individuals and open fraudulent accounts or access existing accounts to carry out unauthorized transactions.
- Loan Fraud: Fraudsters provide false information or documents to obtain loans or credit facilities, often with no intention of repayment.
- Check Fraud: This involves forging or altering checks to withdraw funds from someone else’s account or to deposit counterfeit checks into personal accounts.
- Wire Transfer Fraud: Fraudsters manipulate victims into transferring funds to fraudulent accounts through phishing emails, social engineering, or the impersonation of legitimate entities.
- Insider Fraud: This type of fraud involves employees or individuals with insider access to bank systems who exploit their positions to commit fraudulent activities, such as embezzlement or unauthorized transactions.
What Happens Whenever A Bank Receives A Fraudulent Claim?
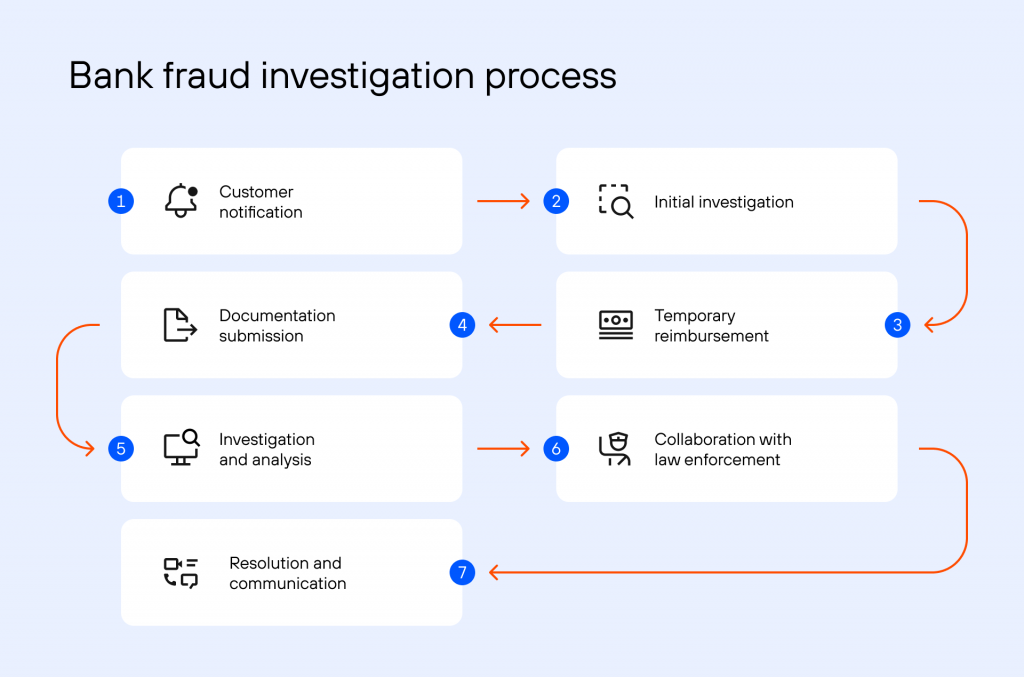
When a bank receives a transaction fraud claim from a customer, they typically follow a step-by-step process to investigate and resolve the issue. The exact process may vary among different banks, but here is a general outline of the steps involved:
- Customer Notification: The customer contacts the bank to report the fraud and files a fraud claim. This can be done through various channels, such as phone, email, or visiting a branch. The bank may have a dedicated fraud reporting hotline or online portal for customers to use.
- Initial Investigation: The bank’s fraud department initiates an investigation into the claim. They gather relevant information from the customer, such as details of the unauthorized transaction(s), any supporting documentation, and account statements.
- Temporary Reimbursement: Depending on the bank’s policies, the customer may be temporarily reimbursed for the disputed amount during the bank investigation. This is known as provisional credit and provides financial relief to the customer while the investigation is underway.
- Documentation Submission: The customer may be required to submit additional documentation or evidence related to the fraud claim. This can include police reports, affidavits, signed statements, or any other information requested by the bank to support the claim.
- Investigation and Analysis: The bank’s fraud department thoroughly reviews the customer’s claim and conducts an internal investigation. They analyze transaction records, account activity, and any available security measures to determine the legitimacy of the claim and identify potential fraudulent activities.
- Collaboration with Law Enforcement: In more serious cases, the bank may collaborate with law enforcement agencies, sharing information and providing assistance to aid in the investigation and potential prosecution of fraudsters.
- Resolution and Communication: Once the investigation is complete, the bank communicates the findings to the customer. If the claim is deemed valid, the bank takes appropriate action, which may include reversing the fraudulent transaction(s), restoring funds to the customer’s account, and updating any related fees or charges.
What Exactly Is A Bank Fraud Investigation?
A bank fraud investigation is a systematic process conducted by banks or financial institutions to identify, investigate, and mitigate instances of fraud. It involves the examination of suspicious activities, transactions, or accounts to determine if fraudulent behavior has occurred. The primary objective of bank fraud investigations is to gather evidence, uncover the perpetrators, mitigate financial losses, and prevent future occurrences. The bank fraud investigation process typically follows these key steps:
Evaluate The Claim
During this stage, the initial review is conducted to evaluate the credibility and severity of the alleged fraud. This may involve gathering information from internal systems, customer interviews, or third-party sources. Investigators gather relevant evidence, such as transaction records, account statements, digital logs, surveillance footage, communication records, and any other documentation that can support the investigation. Investigators employ forensic techniques to analyze the collected evidence and identify patterns, anomalies, or inconsistencies. This may involve data analysis, digital forensics, or collaboration with specialized teams.
Take Preventative Measures To Avoid Further Fraud
Banks are constantly tweaking their anti-fraud processes and techniques to shut down loopholes and vulnerabilities exploited by fraudsters. Banks may take these preventative measures:
- Enhanced Security Protocols: Banks may implement new robust security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and secure login procedures, to protect customer accounts and transactions from unauthorized access.
- Transaction Monitoring: Banks may employ more vigilant monitoring systems that analyze transactional patterns and behaviors to identify any suspicious or fraudulent activity. Real-time monitoring helps detect and block fraudulent transactions promptly.
- Tweak Bank Fraud Detection Systems: Banks may alter their fraud detection systems and utilize machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to identify unusual patterns, anomalies, or deviations from normal customer behavior. These systems flag suspicious activities for further investigation.
- Educate Customers: Banks may educate customers about common fraud techniques, phishing scams, and best practices for securing their accounts. Educational initiatives raise awareness among customers and help them recognize and report potential fraud attempts.
- Fraud Analytics and Risk Assessment: Banks leverage data analytics to assess risk levels associated with customer accounts and transactions. By analyzing various risk factors, banks can proactively identify high-risk activities and take preventive measures accordingly.
- Collaborate and Share Information: Banks may collaborate with industry peers, law enforcement agencies, and regulatory bodies to share information on emerging fraud trends, best practices, and potential threats. This collective approach enhances the effectiveness of fraud prevention efforts.
- Security Audits: Banks may conduct security audits to evaluate the effectiveness of their fraud prevention measures and identify any vulnerabilities or gaps. These audits help banks strengthen their security infrastructure and address potential weaknesses.
- Staff Training: Banks may provide additional training to employees on transaction fraud detection techniques, customer verification processes, and emerging fraud trends. Well-trained staff members are better equipped to identify and prevent fraudulent activities.
Make A Liability Determination
When banks investigate a bank fraud incident, they follow a systematic process to make a liability determination. The exact process may vary among banks, but here are the general steps involved:
- Analysis and Evaluation: The bank’s fraud investigation team analyzes the gathered evidence to understand the nature and extent of the fraud. They assess the account holder’s actions, adherence to security protocols, and any potential vulnerabilities in the bank’s systems or processes.
- Fraud Detection Systems: Banks utilize their fraud detection systems and algorithms to identify patterns, anomalies, or red flags associated with fraudulent transactions. These systems compare the suspicious activity with the account holder’s typical behavior and provide insights into the legitimacy of the transactions.
- Compliance with Regulations: Banks ensure their investigations comply with relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies governing liability determination in fraud cases. They consider legal obligations, contractual agreements, and consumer protection laws that may impact the liability determination process.
- Liability Assessment: Based on the analysis, evaluation, and compliance considerations, the bank makes a liability determination. They assess the responsibility of the account holder, taking into account factors such as adherence to security measures, prompt reporting of fraud, and any evidence of negligence or unauthorized access.
- Communication of Decision: The bank communicates the liability determination to the affected account holder. If the investigation finds the account holder responsible for the fraud, the bank may deny liability.
Reimburse The Customer
If the fraud is legitimate and the customer is not liable, then the bank restores the funds that were fraudulently taken from the customer’s account. The reimbursed amount is credited back to the customer’s account, effectively reversing unauthorized transactions.
Challenges Of Transactions Fraud Detection And Prevention
Fraud detection and prevention are critical for maintaining the integrity and security of financial transactions. However, several challenges exist in effectively combating fraudulent activities. These challenges encompass money laundering, ensuring account protection, secure yet seamless customer onboarding, and the persistent threat of theft of credentials. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of advanced technologies, robust security measures, diligent customer education, and continuous monitoring to stay one step ahead of fraudsters in an increasingly complex digital landscape. By proactively tackling these challenges, financial institutions can safeguard their systems, protect customers, and uphold trust in the financial ecosystem.
Money Laundering
Money laundering is the process of making illegally obtained money appear legitimate by concealing its true origin. It involves a series of transactions to disguise the illicit funds, making them appear as if they come from legitimate sources. Money laundering is often associated with criminal activities such as drug trafficking, fraud, corruption, and organized crime. Here are some common methods used to identify and prevent money laundering:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Financial institutions are required to perform thorough customer due diligence, including identity verification, risk assessment, and ongoing monitoring. This helps identify suspicious customers.
- Transaction Monitoring: Banks and financial institutions employ sophisticated systems to monitor transactions for suspicious patterns or unusual activity. Automated transaction monitoring systems flag transactions that deviate from typical customer behavior.
- Know Your Customer (KYC): KYC procedures require financial institutions to collect and verify customer information, such as identification documents, proof of address, and the nature of their business.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance Programs: These programs include policies, procedures, employee training, and ongoing monitoring of transactions.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity: Financial institutions are obligated to report any suspicious transactions or activities to the appropriate authorities. They may file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) or Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) to alert the authorities of potential money laundering activities.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing: Financial institutions, regulatory bodies, and law enforcement agencies collaborate and share information to identify patterns, trends, and new techniques used in money laundering.
By implementing robust AML measures, conducting thorough due diligence, and reporting suspicious activities, the collective efforts aim to deter, detect, and disrupt money laundering activities, ultimately safeguarding the integrity of the financial system.
Account Protection
Account protection is a significant challenge in preventing bank fraud because of evolving techniques used by fraudsters. Scammers often use phishing emails, fake websites, or phone calls to trick customers into revealing their account information or login credentials. Fraudsters may acquire personal information through data breaches or identity theft, allowing them to pose as legitimate account holders. Hackers also use malicious software, such as keyloggers or remote access Trojans to access customer’s bank accounts.
Customer Onboarding
Customer onboarding poses a challenge in preventing bank fraud due to the need to strike a balance between efficient onboarding processes and robust fraud prevention measures. Banks must gather and verify customer information accurately while ensuring a seamless experience. However, this process can be exploited by fraudsters who provide false identities or manipulate documents. Striking the right balance between customer convenience and effective due diligence is essential to prevent fraudulent activity during the onboarding process.
Theft Of Credentials
The theft of credentials presents a significant challenge in preventing bank fraud due to its potential for granting unauthorized access to accounts. Fraudsters employ various techniques like phishing, malware, or social engineering to acquire login credentials, PINs, or passwords. As credentials are often the primary means of authentication, their theft compromises the integrity of security systems. Detecting and mitigating this type of fraud requires robust user education, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring of account activity to identify suspicious login attempts.
How Do Fraud Victims Recover Their Money?
Will the bank refund unauthorized transactions? In many cases. If you are a victim of bank fraud, maximize your chances of recovering your money by following these steps:
- Contact Your Bank: Immediately notify your bank or financial institution about the fraudulent activity. They will guide you through the process and initiate an investigation into the matter.
- File a Police Report: Report the fraud to your local law enforcement agency. Provide them with all the relevant details and documentation to support your claim.
- Keep Records: Maintain thorough records of all communication, including emails, letters, or phone conversations, with your bank, law enforcement, and any other relevant parties. These records will be valuable evidence during the investigation.
- File a Chargeback: If you notice any unauthorized transactions on your account, dispute them with your bank. They may reverse the fraudulent charges and refund your money.
- Follow Bank Procedures: Cooperate with your bank’s fraud investigation procedures and provide them with any requested information or evidence. They may require you to complete specific forms or provide supporting documentation.
- Report to Regulatory Authorities: Depending on your jurisdiction, you may need to report the fraud to the appropriate regulatory authorities. They can assist in investigating the incident and taking legal action against the fraudsters.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Continuously monitor your bank accounts and credit reports for any suspicious activity. Stay vigilant to detect any future fraudulent transactions promptly.
- Seek Legal Advice: If you encounter challenges or your bank is unresponsive in resolving the issue, consider seeking legal advice from a professional specializing in banking or fraud-related matters.
The specific process and regulations for recovering money lost to bank fraud may vary depending on your location and the policies of your bank. It’s crucial to act swiftly, provide all necessary information, and cooperate with the relevant authorities to increase the chances of recovering your funds.
Why Do Merchants Incur The Costs Of Fraud?
If there is ever a question of who is responsible for bank frauds merchants often get left paying the bill. Merchants end up incurring the cost of fraud via both direct and indirect ways, including:
- Chargebacks: When a customer disputes a transaction as fraudulent, the merchant is usually liable for the chargeback. This means the merchant has to refund the customer and may incur additional fees or penalties. The average chargeback fee is $20 to $100.
- Lack of Fraud Protection: If merchants don’t have adequate fraud prevention measures in place, they become more vulnerable to fraudulent transactions. This can lead to financial losses that the merchant must bear fully.
- Liability Shift: In some cases, liability for fraud can shift to the merchant if certain payment methods or security protocols are not followed. For example, if the merchant doesn’t use secure payment processing methods or fails to comply with industry security standards, they may bear the financial responsibility for any resulting fraud.
- Compliance Requirements: Payment card industry regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), require merchants to maintain secure processing environments. If a merchant fails to meet these requirements and experiences a data breach or fraud incident, they may be held responsible for the associated costs.
- Reputation and Customer Trust: Beyond the direct financial impact, merchants may also experience reputational damage and loss of customer trust following fraud incidents. This can result in decreased customer loyalty, reduced sales, and long-term negative effects on the business.
To mitigate these risks, merchants should invest in robust fraud prevention systems, follow security best practices, monitor transactions for suspicious activity, and stay up to date with industry regulations. Working with payment service providers and implementing advanced fraud detection tools can help minimize the financial burden associated with fraud.
FAQ
How do banks do fraud detection?
Banks employ various techniques for fraud detection, including transaction monitoring, anomaly detection, pattern recognition, machine learning algorithms, and customer behavior analysis, coupled with advanced fraud detection systems and real-time alerts.
What are the steps for fraud investigation?
The steps for fraud investigation typically involve initial detection, evidence collection, analysis, interviews, collaboration with law enforcement if necessary, resolution, and documentation of findings and actions taken.
Will the bank refund the stolen money?
The bank’s refund policy for stolen money depends on the specific circumstances, applicable laws, and the bank’s internal policies. In many cases, if the customer is not at fault and the fraud is reported promptly, the bank will refund the stolen money.
Who is responsible for bank frauds?
Responsibility for bank frauds can fall on various parties. Fraudsters who perpetrate the fraudulent activities are primarily responsible. However, banks also have a responsibility to implement robust security measures, educate customers, and promptly investigate and address fraud incidents. Customers must also exercise caution and follow security guidelines to minimize their vulnerability to fraud.
 PayPal
PayPal Blog
Blog


